Vessel detection and classification in satellite imagery is a fundamental task in multiple applications, from maritime surveillance to maritime traffic management. This technology makes it possible to monitor large areas of water efficiently and obtain valuable information about maritime activity.
Vessel detection consists of identifying the presence of a ship in a satellite image. Traditionally, image processing techniques based on features such as shape, size and contrast have been used. However, in recent years, deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have revolutionized this field, enabling more accurate and robust detection.
Key challenges in classification:
- Limited visual variability: Many types of ships can have a similar appearance, making them difficult to distinguish.
- Occlusions Part of the ship may be obscured by other objects or water, reducing the available information for classification.
- Scarcity of data One of the biggest challenges is the scarcity of labeled data to train classification models. Obtaining high-resolution satellite imagery with accurate annotations of different ship types can be costly and laborious.
The scarcity of labeled data is a common problem in many fields of computer vision, and ship classification is no exception. Training a deep learning model requires a large amount of data to generalize and avoid overfitting.
Strategies to address this problem:
- Data augmentation: Applying data augmentation techniques to generate new images from existing ones, such as rotations, scaling, cropping, and brightness changes.
- Transfer learning: Utilizing pre-trained models on large datasets (like ImageNet) and adapting them to the specific task of ship classification.
- Active learning: Intelligently selecting images to label to maximize model performance with minimal effort.
- Synthetic data generation: Creating synthetic images of ships using 3D rendering tools
- Few-Shot Learning:The combination of techniques and classification models allows this type of work to be carried out even with a very small number of reference images.
Model Inputs
In the case of SEDA, the Learning with Few Examples technique was chosen, since the number of reference images was so low that the other techniques were unfeasible.
The Few-Shot Learning: is a branch of machine learning that seeks to train models with a limited number of labeled samples. In the context of vessel detection in satellite imagery, this involves developing models capable of identifying new vessel types with only a few training samples.
The ideal characteristics for this type of learning, and that therefore the model input data must meet, are the following. High Resolution, to be able to perform accurate vessel detection it must be greater than 0.5m/px. In addition, the use of high resolution facilitates the extraction of features from the element, allowing more accurate comparisons between them. On the other hand, the optical images provide a detailed visual representation of the objects, so for this particular use case, it would be ideal to use this type of image.
Model outputs
SEDA includes a solution based on Convolutional Neural Networks to analyze high-resolution optical images, generating as output the detection of the searched element. This element will be provided by the user previously in a ZIP file containing the reference images of the ship being searched.
The following image shows an example of the reference ship that is intended to be searched:

Here is the result of the detected vessel in a Pleiades Neo image.
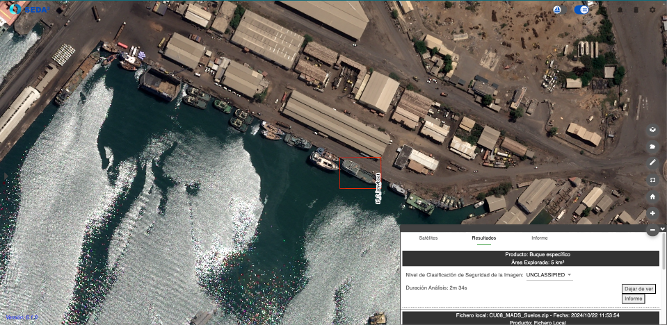
As a result, SEDA offers the possibility to download reports in customized formats such as PowerPointor reports in standardized formats such as KML, NVG o ShapefileIn addition, reports in NATO formats such as ISRSREP y RECCEXREP format are also available NSIF.
Applications
This type of detection has a wide range of practical applications. In the maritime field, this technology allows real-time monitoring of maritime traffic detection of illicit activities such as illegal fishing or human trafficking, and assessment of the environmental impact of maritime operations. In the defense and maritime surveillancethe threat detection and infrastructure protection critical.

