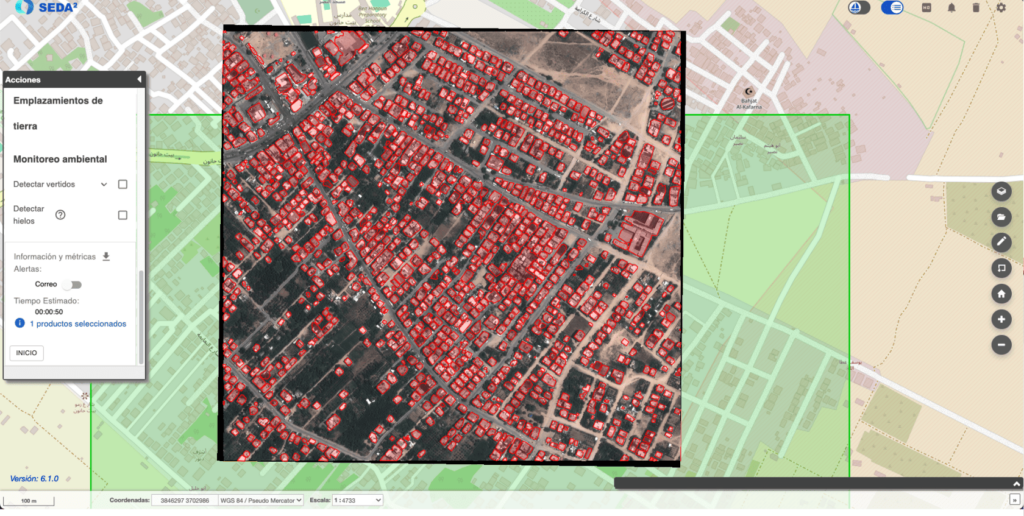
Buildings segmentation
Building vectorization, specifically through the detection of rooftops in high-resolution (HR) and very high-resolution (VHR) satellite images, is a key process in various fields, both civil and military. This approach allows for precise identification of building footprints using images with resolutions as fine as 1.5 meters per pixel.
The use case implements a Deep Learning algorithms for the automated detection of rooftops in satellite images, facilitating accurate building vectorization. This process is essential in sectors such as:
- Military domain:Enhances geospatial intelligence and strategic planning, enabling more precise and efficient decision-making.
- Urban planning:Useful for updating and maintaining geospatial databases of cities.
- Disaster management:Helps identify damaged buildings after natural disasters to optimize response and reconstruction efforts.
The model, integrated into the SEDA geospatial intelligence platformis based on a CNN U-Net architecture to segment rooftops. This improves accuracy and efficiency, reducing the required human intervention and speeding up the geospatial analysis process.
The vectorization process generates the following output reports:
- Vector maps:Polygons representing the detected rooftop footprints.
- Geospatial visualization:Maps showing the location and shape of detected buildings overlaid on satellite images.
These results can be exported in standard geospatial formats (such as GeoJSON or Shapefile) for integration into other geographic information systems (GIS). GeoJSON o Shapefilefor integration into other geographic information systems (GIS).
Applications
- Military intelligence:Allows for the detection, mapping, and analysis of structures of interest in strategic areas to improve planning and surveillance.
- Cartography and urban planning:Automatically updates maps of cities and rural areas, providing more accurate information for infrastructure management.
- Disaster management:Useful for identifying buildings affected by natural disasters like earthquakes or hurricanes, enabling a faster response.
- Sustainability and environmental analysis:Allows for the assessment of urban growth and its impact on the environment by comparing construction areas over time.
The automatic vectorization of buildings through HR and VHR satellite images is a powerful and versatile tool that can be applied in multiple sectors. The use of Deep Learning algorithms not only improves detection accuracy but also optimizes the resources needed for geospatial analysis. This approach offers a robust solution to meet needs in both military and urban management and emergency response.

